Which of the Following Best Describes a Lewis Base
Which of the following terms describes the reactivity of boron tribromide BBr 3. Lewis acids and bases result in the formation of an adduct rather than a simple displacement reaction as with classical acids and.

Possible Multiple Choice Questions
A Lewis base is therefore an electron-pair donor.

. Which of the following describes Ka for the water. So they does not donate electron. Strong base weak base strong acid weak acid.
In like manner the original base accepts a proton and becomes a conjugate acid. A Lewis base then is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. A By definition this.
Which statement describes the Arrhenius interpretation of acids and bases. As a result hydrogen bonds with nitrogen atom. CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base and BBr3 can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Therefore the Lewis base here is CO. Chemistry questions and answers. A Brønsted-Lowry acid and Lewis acid B Brønsted-Lowry base and Lewis base C Lewis acid and not a Brønsted-Lowry acid D Lewis base and not a Brønsted.
When a Lewis base donates an electron pair to get H it accepts a proton and thus is a Bronsted base. Lewis Acids and Bases. A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor.
The reaction of Lewis acid-base can be represented by the transfer of pairing electrons to an acid medium from a base. So if a Lewis base acquires a proton it is also a Bronsted base. According to Lewis a base is a substance or specie which is able to donate electrons.
Lewis bases are the one which donate electrons. Soluble metal salt and carbon dioxide. An atom ion or molecule with a lone-pair of electrons can thus be a Lewis base.
The difference is context-specific and varies based on the reaction. What best describes a bronsted lowry acid base reaction. Which best describes the definition of Lewis acids and bases.
Among the given compounds 3 and 4 are acids as they have alcohol. In a Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction the original acid gives up its proton and becomes a conjugate base. CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base BBr3 can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid and CH3Cl can be a Lewis base.
CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base. To make it simple it is a substance through which a pair of electrons is donated to form a covalent bond. For every acid there is a conjugate base and for every base there is a conjugate acid.
BBr3 can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid. Then I associate Lewis acids with Bronsted acids by process of elimination. A chemist lectures about the following definition for acids and bases.
A Lewis base is a substance that donates a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. See answers 2 Best Answer. Which of the following terms describes the role of ethanol in the acid-base reaction shown.
Some molecules can act as either Lewis acids or Lewis bases. OH C1 CCH33 اختر احدى الاجابات A. While other molecules like BCl 3.
Lewis bases are electron pair acceptors. Which of the following best describes a chemical species that is measured to have Kb32x10-18. You can bond with either H or something else.
A SiH 4 B HCl C H 2 S D PH 3. Each of the following anions can give up their electrons to an acid eg OH- CN- CH_3COO- NH_3. This states that a Lewis base is a nucleophile.
Which of the following statements about Lewis bases is true. A base is a substance in a solution that captures hydrogen ions and raises the pH. Since Lewis bases are electron-rich species that have the ability to donate electron-pairs they can be classified as nucleophiles.
For example NH3 is a Lewis base. CH3Cl can be a Lewis base. The second one is ethers which is having oxygen with two lone pair of electrons and acts as a Lewis bases.
NOT the ability of bases to release hydrogen ions into solution. The most common Lewis bases are ammonia alkyl amines and other conventional amines. Correct option is B Carbon molecules which have pie electrons ie multiple bonds of a carbon have more electron density in that bond which can be easily donated to other species so they generally act as lewis base.
C Acid base conjugate base conjugate acid. Acid base conjugate base conjugate acid. AlCl3 BF3 and CO2 are Lewis acids as they accept a pair of electrons from another species during the formation of a co-ordinate bond.
They utilize the highest occupied molecular orbital or HOMO Figure 2. Gilbert Lewis 1875-1946 proposed a third theory of acids and bases that is even more general than either the Arrhenius or Brønsted-Lowry theories. The first one is the formula of aldehyde or ketone which is having a C - O-bond.
Lewis Bases are Nucleophilic meaning that they attack a positive charge with their lone pair. C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 O. Therefore when ammonia is dissolved in HCl it will accept the hydrogen atom as nitrogen gave electron to the hydrogen atom.
A Lewis acid is an electron -pair acceptor. Asked Sep 30 2016 in Chemistry by BustaRhyme. Suppose a large organic molecule X is classified as a Lewis acid while another large molecule Y is classified as a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Which of the following best describes the role of AlCl3 in Friedel-Crafts reactions اختر إحدى الخيارات A Lewis base catalyst B Nucleophile C Catalyst to direct meta D Lewis acid catalyst What is the IUPAC name of the following compound. A Lewis base is a donor of electron-pair. Commonly Lewis bases are anionic in nature and their base strength generally depends on the pK a of the corresponding parent acid.
So I think we have enough context now. A Lewis acid is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. Lewis bases are electron pair donors.
For example is a lewis base because nitrogen has a lone pair of electron. One advantage of the Lewis theory is the way it complements the model of oxidation-reduction reactions. Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0 Add a Comment.
A Lewis base is any substance such as the OH-ion that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis acid is a substance that accepts a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. HCl and Ag are have less electron density in their molecules so they cannot donate pair of electrons hence they are not.
Which of the following compounds has the highest pK a.

Chem 180 Set 2 Flashcards Quizlet
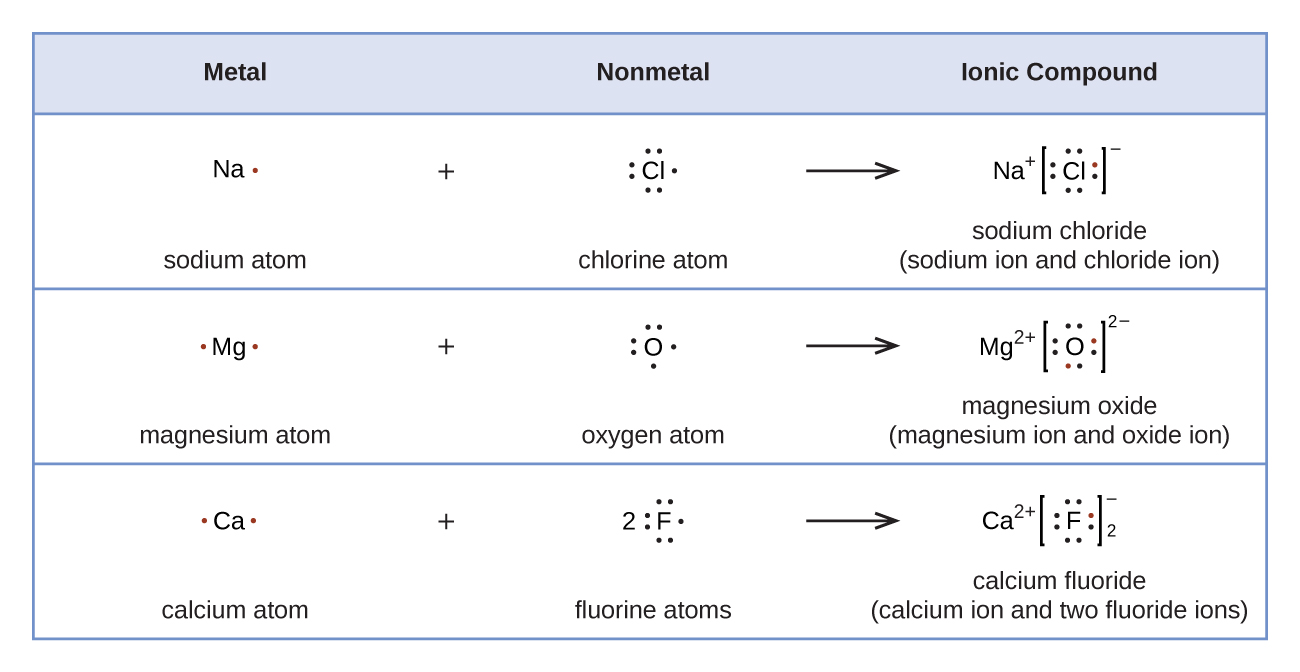
7 3 Lewis Symbols And Structures Chemistry

Draw A Lewis Structure Of Formaldehyde Lewis College Life Hacks Middle School Science

Ben Giles Blooming Books 750 Piece Shaped Jigsaw Puzzle Bloom Book Shaped Jigsaw Puzzles Shape Puzzles

Chapter 3 Ionic And Covalent Compounds Chapter 3 Ionic And

Question Video Recalling The Color Produced By An Alkali Metal In A Flame Test Nagwa

The Lewis Definitions Of Acids And Bases

David Chalk Teacherchalky1 Twitter Middle School Science Activities Teaching Biology Medical Student Study

Organic Chemistry 331 Sapling Learning Ch 4 Flashcards Quizlet

Chem 180 Set 2 Flashcards Quizlet

7 3 Lewis Symbols And Structures Chemistry

Organic Chemistry 331 Sapling Learning Ch 4 Flashcards Quizlet

Organic Chemistry 331 Sapling Learning Ch 4 Flashcards Quizlet

Rates Of Reaction The Effects Of A Reactions Graphing Energy Activities

A P Ii 20 21 Lab Flashcards Quizlet
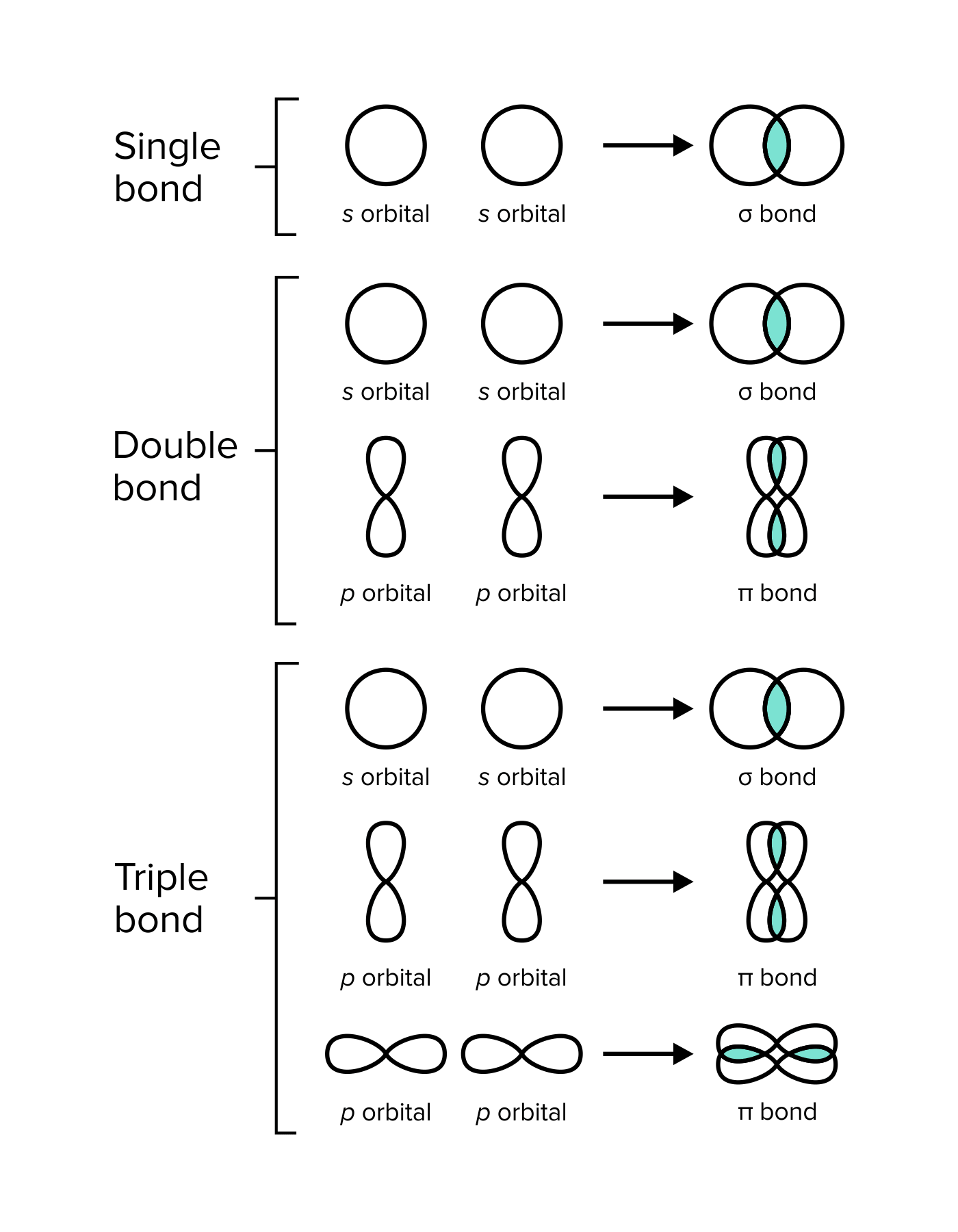
Bonds And Interactions For The Mcat Everything You Need To Know Shemmassian Academic Consulting

Gene Simmons Describes The Most Profound Capitalist Lesson He Ever Learned Gene Simmons Gene Simmons Kiss Gene Simmons Costume

Lewis Acids And Bases Lewis Acids And Bases Teaching Chemistry Organic Chemistry

Comments
Post a Comment